Shapes
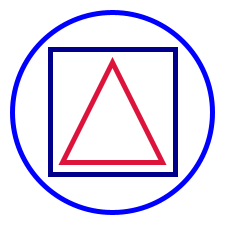
You can easily create basic geometric shapes by calling methods on the Picture object. Here's an example showing a circle, square, and triangle.
import doodle.core.*
import doodle.java2d.*
import doodle.syntax.all.*
val basicShapes =
Picture
.circle(200)
.strokeColor(Color.blue)
.on(Picture.square(125).strokeColor(Color.darkBlue))
.on(Picture.triangle(100, 100).strokeColor(Color.crimson))
.strokeWidth(5.0)This program gives the output below.
The Shape algebra provides the following methods, which you'll find on the Picture object of whichever backend you're using:
emptycreates the empty picture that takes up no space and renders nothing. Useful for that sweet monoid identity and for the base case in recursions.square(sideLength)creates a square with the given side length.rectangle(width, height)creates a rectangle with the given width and height.circle(diameter)creates a circle with the given diameter. Specified in terms of diameter rather than radius so thatsquare(100)andcircle(100)take up the same space.triangle(width, height)creates an isoceles triangle with the given width and height.
Also on the Picture object you'll also find some more complex shapes, which are provided by the Path algebra:
equilateralTriangle(sideLength), which creates an equilateral triangle with the given side lengthregularPolygon(sides, radius)creates a regular convex polygon with the given number of sides, and the distance from the center to each vertex (also known as the circumradius) is given by the radius.roundedRectangle(width, height, radius)creates a rounded rectangle with the given width and height, and corners created from quarter circles of the given radius.star(points, outerRadius, innerRadius), which creates a regular star polygon with the given number of points. The distance from the center to the farthest point is given by the outer radius, and the distance from the center to the closest point by the inner radius.
This example demonstrates a mixture of regular polygons and stars.
def polygon(size: Int): Picture[Unit] =
Picture
.regularPolygon(5, size)
.strokeColor(Tailwind4Colors.amber400)
def star(size: Int): Picture[Unit] =
Picture
.star(5, size, size / 2)
.strokeColor(Tailwind4Colors.sky500)
val complexShapes =
polygon(60)
.on(star(70))
.on(star(90))
.on(polygon(80))
.on(polygon(100))
.on(star(110))
.strokeWidth(7.0)The resulting image is below.

Implementation
These methods are available on all backends and Image. The underlying algebras are Shape and Path.